Extrusion Blow Moulding
The extrusion blow moulding is used for production of hollow objects in large quantities, like bottles and similar containers, and it’s also easily adaptable for other items ranging from childrens toys to engineering components.
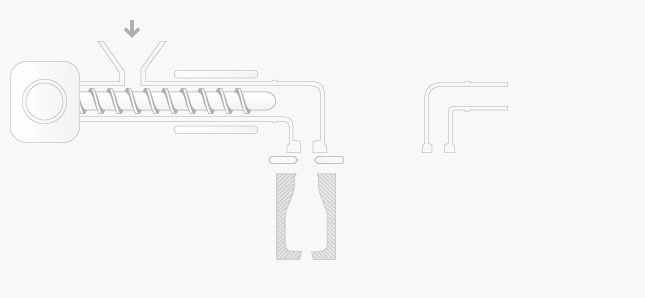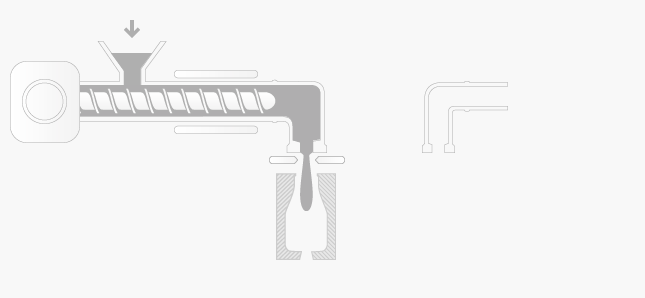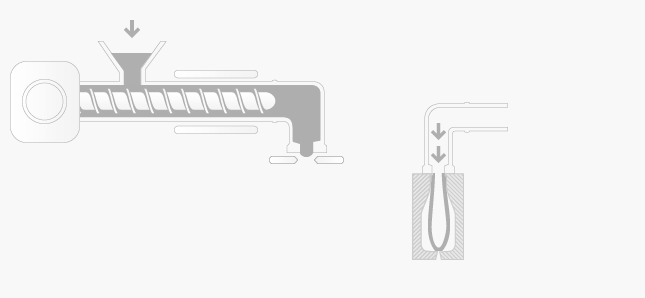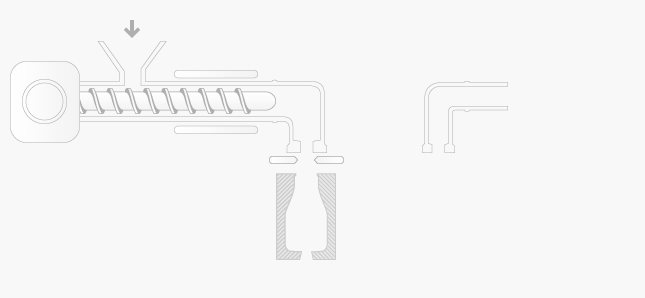
The extrusion blow moulding process consists of the following sequence of operations:
-
plasticised polymer is extruded as a hollow pipe called a parison
-
the parison is cut to length and clamped in the blow mould
-
the blow mould is passed to the air pipe and the parison is given a blast of air
-
air inflates the hollow parison and forces it against the sides of the mould
-
after a short cooling period, the moulding is ejected
Typical plastics used for extrusion blow moulding:
- PP (Polypropylene)
- HDPE (High Density Polyethylene)
- LDPE (Low Density Polyethylene)
- PC ( Polycarbonate)
- PETG
Stretch Blow Moulding
Stretch blow molding is best known for producing PET bottles commonly used for water, juice and a variety of other products.
One of the major advantages of stretch blow molding is the ability to stretch the preform in both the hoop direction and the axial direction. Stretch blow molding is divided into two different categories single-stage and two-stage.
Two-stage stretch blow molding is the same as single-stage, except the preforms are already made.
Two-stage stretch blow moulding process is following:
-
preform re-heated and placed into a mold where forming takes place
-
in forming process the preform is stretched with a rod and inflated by air
-
the plastic piece is removed from the mold after it cools and hardens
Plastics used for stretch blow moulding:
- PET (Polyethylene – Terephthalate)
- PS (Polystyrene)
Injection Moulding
Injection moulding is a widely used in manufacturing, as it’s a quick way of producing large numbers of identical components such as plastic closures, covers, handles, trays and etc.
Injection molding consists of high pressure injection of the raw material into a mold which shapes the polymer into the desired shape.
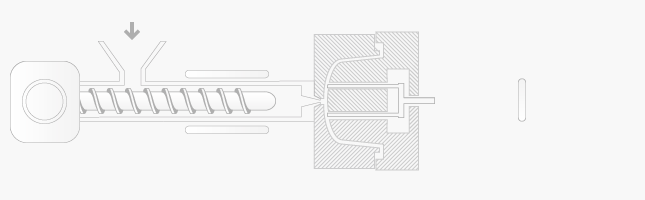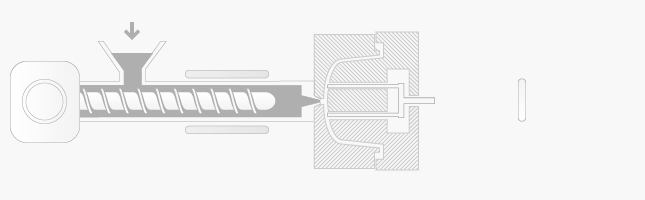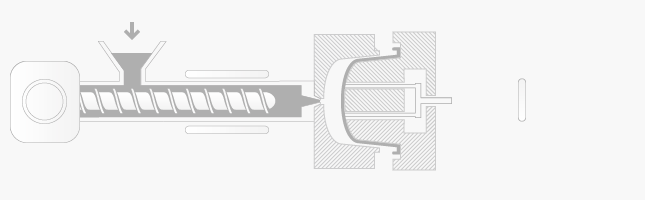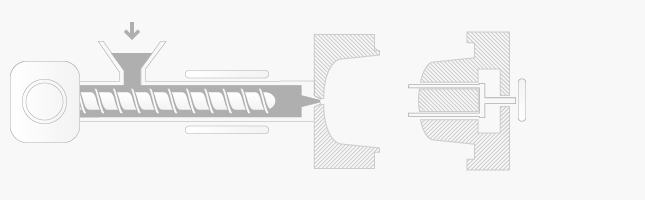
Injection moulding process is following:
-
plastic granules are fed from the hopper into barrel and rotating screw of the injection moulding machine
-
plastic granule using heat, friction and force converts into molten plastic liquid
-
the screw is forced forward and molten plastic is injecting into the closed mould tool and using pressure while all spaces of mould are filled
-
the plastic injection moulding tool is held closed under pressure to allow the plastic material to cool and set hard in the mould tool cavity
-
opening and ejection – the screw begins moving back for the next moulding tool, the tool is open and the use of of air blast, plate or rods, finished plastic moulding is ejected
Most thermoplastics can be injection moulded, including:
- PP (Polypropylene)
- HDPE (High Density Polyethylene)
- LDPE (Low Density Polyethylene)
- GPPS (Polystyrene)
- PC (Polycarbonate)
Extrusion Blowing
-
blown film is created when the molten plastic material (or melt) is extruded through a ring-shaped die to form a continuous tube of plastic which is simultaneously inflated with air to form a plastic bubble.
-
the bubble must be maintained at a constant pressure throughout the production run.
-
the bubble is carried through variable speed rollers to the point where it reaches the required size and is cooled by air to convert it into a solid film tube of the desired thickness or gauge.
-
the tubing is then guided by pinch rolls to become ‘Lay Flat’ film which is wound, slit and trimmed automatically before being converted into a wide range of film and bag products – often involving printing and sealing.
Plastics used for extrusion moulding include:
- LDPE (Low Density Polyethylene)
- HDPE (High Density Polyethylene)
